
Project
Photo: UNFCCCMonitoring the UN Climate Negotiations
As changes in climate become more extreme, their affects are being hardest felt throughout developing countries. Since 1994, the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change has laid out actions to limit the increase of global average temperatures and confront the impacts of climate change.
The States that are Parties to the Convention meet every year in the so-called Conference of the Parties (COP) to review their commitments, the progress made in fulfilling them, and pending challenges in the global fight against the climate crisis.
At COP21 in 2015, they adopted the Paris Agreement, which seeks to strengthen the global response to the climate emergency, establishing a common framework for all countries to work on the basis of their capacities and through the presentation of Nationally Determined Contributions (NDC) that will:
- Limit the increase in global temperatures to 2°C compared to pre-industrial levels and continue efforts to limit it to 1.5°C;
- Increase the capacity of countries to adapt to the impacts of climate change; and
- Ensure that financing responds to the goal of reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Our focus areas
THE CLIMATE CRISIS AND HUMAN RIGHTS
The climate crisis, due to its transversal character, has repercussions in various fields, geographies, contexts and people. In this regard, the Preamble to the Paris Agreement states that it is the obligation of States to "respect, promote and fulfill their respective obligations on human rights, the right to health, the rights of indigenous peoples, local communities, migrants, children, persons with disabilities and people in vulnerable situations and the right to development, as well as gender equality, the empowerment of women and intergenerational equity."
AIDA at the COP
COP25: Chile-Madrid 2019
At COP25 in Madrid, Spain, we advocated for the inclusion of the human rights perspective in various agenda items. We promoted the incorporation of broad socio-environmental safeguards in the regulation of Article 6 of the Paris Agreement, which refers to carbon markets. We closely followed the adoption of the Gender Action Plan, as well as the Santiago Network, created "to catalyze technical assistance […] in developing countries that are particularly vulnerable to the adverse affects of climate change." We also encouraged the inclusion of ambitious and measurable targets for the reduction of short-lived climate pollutants in the climate commitments of States.
Related projects

"No thank you" says the Green Climate Fund Board to transparency and civil society input
By Andrea Rodríguez, legal advisor, AIDA,@arodriguezosuna Once again civil society organizations expressed disappointment at the lack of transparency and civil society engagement at the latest meeting of the board of the Green Climate Fund (GCF), an operating entity of the United Nations Convention Framework for Climate Change (UNFCCC). The 24-member board met June 25-28 in Songdo, South Korea to further advance a process of putting the GCF into operation. The GCF will operate as a mechanism for transferring funds from the developed to developing world in order to help developing countries finance adaptation and mitigation practices to combat climate change. Civil society organizations have been constantly asking the GCF board for better opportunities for civil society to effectively be involved in the GCF decision-making process. Organizations have sent letters to board members, advisors and the GCF Interim Secretariat. But these many attempts to draw attention and consideration to civil society’s concerns have come to no avail. The board has constantly closed the doors to civil society’s active and effective participation. At board meetings, civil society may only have two active observers in the meeting room: one representing the north and the other the south. The other accredited observers have to sit in an overflow room to watch the meeting. The two active observers may only engage in the meeting if invited by the co-chairs of the board. Only one intervention can be made per each agenda item of the meeting and for no more than three minutes each time. On the last day of the Songdo meeting, the co-chairs disallowed any interventions from civil society, claiming there was not enough time. Ironically, the most important decisions were made on the last day. Given these limitations imposed by the co-chairs, the two active observers in the meeting room approached several board members to share key points on different papers from the perspective of civil society. The co-chairs, however, penalized this action and forbade the active observers from talking to board members. Despite the frustration of the being undermined and excluded, civil society was hoping to win at least one battle at the meeting: getting the board to decide in favor of live webcasting. Live webcasting shows a commitment to accountability and transparency. It provides opportunities for people without the resources to travel to board meetings to get involved in the meeting while also limiting the CO2 emissions generated by each board meeting through a reduction in the number of international flights taken for attendance. Webcasting is widely used by climate-related funds and is even used by the UNFCCC, the international environmental treaty of which the GCF is part. In Songdo, the GCF board decided against live webcasting on the argument that it would be too expensive at US$20,000 to US$30,000 per meeting. The board’s reference prices, however, are far more than the market average of US$1200 per day. According to the Adaptation Fund (AF) Secretariat and its webcast provider, live-streaming of AF board meetings costs about $1,000-$1,250 per day of broadcast, depending on site specific issues. Instead of live webcasting, the GCF board agreed to make webcasts of the meeting accessible three weeks after the event upon registration. Civil society organizations believe that this three-week delay prohibits organizations from advocating on the issues related to the discussions and decisions at the meeting. The Green Climate Fund has decided to have a strategic focus on climate mitigation and adaptation and seek to maximize sustainable development. Nevertheless, it is difficult to understand how the fund would ever be able to maximize “sustainable development” if its decisions are not made with the support of effective stakeholder participation and engagement throughout the whole process.
Read more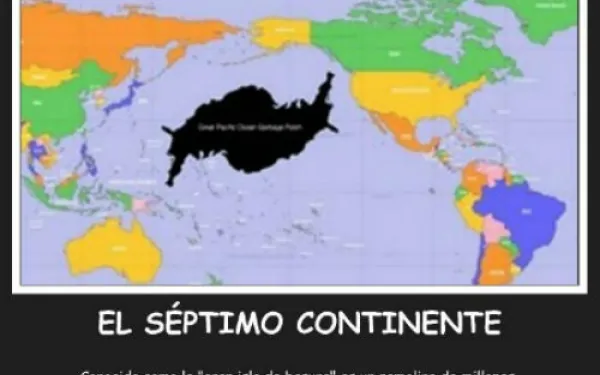
There is a blot in the middle of the ocean…
By Florencia Ortúzar, legal advisor, AIDA The first time I heard about the mysterious “rubbish island” I was shocked. How could a huge floating mass as big as a country go unnoticed in the ocean without being on everyone’s lips? Incredibly, many people haven’t even heard of this Pacific Trash Vortex that grows larger every day, making it the world’s largest rubbish dump. A soup of what? The Great Pacific Garbage Patch, as it’s officially known, is one of the five floating rubbish dumps polluting our world’s oceans. It was the first to be discovered and is the biggest. It’s located in the middle of the Pacific Ocean between the U.S. states of Hawaii and California, about 1,000 kilometers off the coast of Hawaii. The size of the rubbish heap is difficult to determine. Estimates range from about 15,000 square kilometers (equivalent to the surface area of Antarctica or 8.1% of the Pacific Ocean) to 700,000 square kilometers (almost the surface area of Chile). Let me explain a little more about this sad and unusual phenomenon. The island of rubbish is not a solid island as such, nor a floating sheet of trash. Rather, it’s a soup of plastic particles floating in a gyre. Ocean currents collect thousands of tons of floating garbage and round them up in a giant vortex. The slowly rotating mass prevents the rubbish from dispersing. This soup has everything: abandoned fishing nets, plastic bottles, caps, toothbrushes, shoes and much more. But more than anything, the vortex consists of small particles of plastic created when the waves and sun break down larger pieces. This gigantic mass remains below the surface of the water in a column estimated to extend 30 meters deep. Paradoxically, despite its huge size, the rubbish dump is not easy to visualize as a whole and has not been captured in satellite images because of its location under the water. Worse, it is located in international waters, so no nation is responsible for the waste. After concerned scientists and environmentalists, the only people left to help clean up the mess are passengers on special cruise ships who visit the vortex to help remove some of the rubbish. In all, it’s a gigantic mess going unnoticed, growing slowly but surely in a no man’s land devoid of a god or the rule of law. A chance discovery In 1988, experts from the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration predicted the existence of the garbage patch in the North Pacific Ocean by analyzing local marine currents. But it wasn’t until a decade later when oceanographer Charles Moore officially discovered the trash heap, which was dubbed the "Eastern Garbage Patch." In July 1997, Captain Moore was sailing through the North Pacific Gyre when he came across miles and miles of synthetic pieces of debris, and an immense mass of floating garbage. It took the American one week to cross the accumulation of waste. In 1994, Moore established the foundation Algalita Marine Research to focus on the protection and regeneration of kelp forests and wetlands along the coast of California. But after his floating garbage island discovery, Moore dramatically changed the course of his foundation and dedicated it to raising awareness and promoting education about the garbage patch. (See Moore’s TED talk). Expeditions to the forgotten island Since its discovery, there have been various scientific expeditions to the Great Pacific Garbage Patch and other floating garbage islands like it. Unfortunately, these trips have not managed to generate a significant amount of public awareness or impact outside environmental circles. Nobody seems to be willing to take responsibility or action. The most recent expedition in May was organized by the Society of French Explorers (in French) on a schooner called L’Elan, assisted by Captain Moore on board. The results of the mission have not yet been published. Hopefully now with the ability of social networks to disseminate information widely, the issue will generate more interest and make people aware of the huge amount of plastic we consume. What can we do? As mentioned above, the garbage island mainly consists of billions of plastic pieces too small to be seen. This makes it difficult for the debris to be removed from the ocean. You would have to put a very fine net across the surface of the water, which would disturb the ecosystem and essential marine fauna such as plankton, a key food source for ocean animals. What is more, accessing the polluted area would require a considerable amount of resources including manpower and expensive materials to undertake the difficult work out in the open seas. The task becomes even more unlikely where you consider that the garbage island is located in international waters where no country is sovereign (the tragedy of the commons). For now and until we come up with new technology that lets us travel back in time to prevent this disaster, the best and most sensible thing to do is to stop producing so much garbage, and especially to limit our consumption of disposable plastic. It is also important to help raise awareness of the problem so more people understand the effects of their consumerism, change their lifestyles and educate future generations who will be looking after the planet. The island of trash consists of materials that at one time helped revolutionize the world. Today we are surrounded by plastic: we eat and drink from it. We use it every day. It is present in nearly all of our activities. Plastic is almost a miracle product. Cheap, effective and virtually indestructible, it doesn’t break. It just disintegrates into smaller parts. The considerable durability of plastic means that almost all the plastic molecules ever created still remain somewhere on the planet. Now at least we have a better idea on where they end up: on rubbish island.
Read more
Peru and its socio-environmental conflicts
By María José Veramendi Villa, legal advisor, AIDA, @MaJoVeramendi “In Peru, the general state of social conflict is strongly influenced by the dynamics of economic growth that the country has experienced in recent years; but this growth has not necessarily brought measures that generate a perception of social welfare or political representation for certain sectors of society. ” (Ombudsman’s report No. 156: Violence in social conflict, March 2012) Peru is rich in minerals and other natural resources. Evidence of this is that as of June 2012, 20.3% of the national territory was licensed for mining activities, according to a report by the Cooperación NGO based on data from the government’s Geological Mining and Metallurgical Institute (INGEMMET). In June 2013, the Ombudsman of Peru released its Monthly Report on Social Conflict No. 112 (in Spanish). The report lists 223 registered social conflicts: 170 of which are active (76.2%) and 53 latent (23.8%). While there was a decline in the number of conflicts from the previous month, the most significant and prevalent type of conflict was socio-environmental, of which there were 145 cases in June. Of those cases, 105 were in mining, 18 in hydrocarbons, eight in energy activities and four in forestry projects. The Ombudsman’s office defines social conflict as “a complex process in which different sectors of society, the state and the private sector have conflicting objectives, interests, values or necessities, and that these contractions can lead to violence.” Causes In the 2007 report Socio-environmental Conflicts from Extractive Activities in Peru (in Spanish), the Ombudsman´s office identified at least five causes of these conflicts: People’s justified fear that extractive activities like mining can potentially cause contamination; Communities feel vulnerable living in areas where these activities are being developed; People lack trust in the government’s ability to prevent the contamination and degradation of the environment where they live; Concerns that weak regulations and controls on extractive activities can cause contamination resulting in collateral damages to third parties, imposing higher costs on activities like agriculture, whose existence and development can be jeopardized by the decline in quality or quantity of available water; and The negative impacts of extractive activities. These causes are as pertinent today as they were in 2007. But the Peruvian authorities still appear to ignore the situation, and, in response, the justified fear of the population and the mistrust in the state worsen. A recent example: The implementation of prior consultation Convention No. 169 (in Spanish) of the International Labour Organization (ILO) came into force in Peru on February 2, 1995. Since then the country has been obligated to comply with its provisions, which enforce, among others, the right of indigenous and tribal peoples to be consulted onissues that affect them. The convention also states that these people, in a prior, free and informed manner, can participate in the processes to develop and formulate policies that affect them. According to the jurisprudence of the Peruvian Constitutional Court, the convention has constitutional status. Despite this, its implementation was non-existent to the point of being a systematically denied right in the country until August 23, 2011. That’s when the Peruvian Congress approved legislation on the right to prior consultation for indigenous and tribal peoples. The law was promulgated and published on the September 6, 2011, and it has been in effect since December of that year. The Rules of Procedure to apply the Law were issued on April 3, 2012 and put into force a day later. But these legal instruments, which could be seen as an act of good faith to implement norms that already exist in our legal system, have been heavily criticized for technical failures and for reducing the standards of protection achieved by indigenous people through their many years of struggle. These protections were cemented in the ILO Convention No. 169 of 1989, the United Nations Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples (2007) and in the jurisprudence of the international bodies set up to protect human rights, especially the Inter-American Court of Human Rights I want to highlight two facts on these shortcomings: First, the Rules of Procedure of the Consultation Law only applies to acts conducted after its approval. This means that during the 16 years between the approval of Convention No. 169 and the Consultation Law and its Rules of Procedure, the former was merely a decorative instrument. The second little-known fact is that the Judgment 00025-2009-PI/TC (in Spanish) of the Constitutional Court states specifically: “The enforceability of the right to consultation is linked to the implementation of the ILO Convention 169 in our legal system." Government officials (in Spanish) have signaled that the Law of Prior Consultation is not binding. Even the Peruvian president said the law “should be viewed as an instrument allowing investment, and to not to be seen as an obstacle.” We remember that in the case of The Kichwa Peoples of Sarayaku Vs. Ecuador, the Inter-American Court of Human Rights ruled that proper consultation is a general principle of international law. It’s time to be alert. The proper implementation of the right to consultation and prior, free and informed consent is the key to developing effective protection of indigenous rights. In a country where socio-environmental conflict is the norm – along with the causes mentioned above, it is essential to build trust and confidence among the population and give assurances that their rights will be safeguarded. If these points are not put into action, it would be no surprise to see a surge of conflicts in future.
Read more