
Project
Liliana Ávila /AIDAMayan women’s struggle before the Inter-American Development Bank in Guatemala
Mayan communities succeeded in getting the IDB Invest to develop a responsible exit plan after withdrawing its financing for two hydroelectric projects that negatively impacted ecosystems and the livelihoods of indigenous peoples, especially women, in the micro-region of Yichk'isis (Ixquisis).
In the struggle to defend their water, territory and way of life, indigenous Mayan communities in the Yichk'isis (Ixquisis) micro-region of northern Guatemala convinced the Inter-American Development Bank Group to withdraw its financing of two hydroelectric dams whose implementation violated their rights. The decision was also significant in that the IDB, for the first time, designed a responsible exit plan.
That historic advance was the result of the complaint that the communities filed in August 2018—with the support of AIDA, the Plurinational Ancestral Government of the Akateko, Chuj, and Q'anjob'al Native Nations, and the International Platform against Impunity. The complaint was filed with the Independent Consultation and Investigation Mechanism (MICI), the IDB Group's accountability office.
In resolving the case in September 2021, the MICI concluded that IDB Invest failed to comply with its own operational policies and safeguards, in the framework of the financing granted to the company Energía y Renovación S.A. for the implementation of the San Mateo and San Andrés hydroelectric projects.
Learn more about this achievement
In the mountains of Northwestern Guatemala, near the border with Mexico, the land is rich and fertile. Several important rivers and many other water sources feed the soil.
The residents of these mountains, many indigenous women of Mayan descent, have long depended on the waters to nourish them, to provide them with fish, as well as for agriculture, sanitation, and cooking.
But the construction of the San Mateo and San Andres dams has caused water scarcity and the contamination of rivers and other natural resources long cherished by the communities.
The near lack of water has also drastically reduced harvests, lessening the income gained from selling corn, wheat, beans, coffee, sugar cane and other products in the market. As a result, the conditions of poverty in the area have deepened.
And the risk situation is profound, particularly for women, who have played a very important role in the defense of water and territory threatened by hydroelectric projects, and are therefore victims of intimidation and stigmatization.
As guardians of their land and water, they have come to its defense and they’ll continue to prevent environmental deterioration from further harming their families.
Read our fact sheet on the case

Related projects
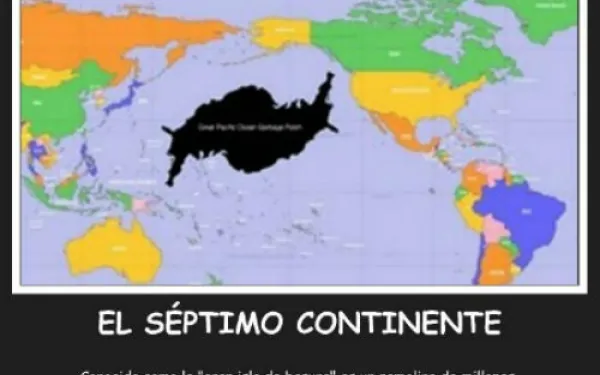
There is a blot in the middle of the ocean…
By Florencia Ortúzar, legal advisor, AIDA The first time I heard about the mysterious “rubbish island” I was shocked. How could a huge floating mass as big as a country go unnoticed in the ocean without being on everyone’s lips? Incredibly, many people haven’t even heard of this Pacific Trash Vortex that grows larger every day, making it the world’s largest rubbish dump. A soup of what? The Great Pacific Garbage Patch, as it’s officially known, is one of the five floating rubbish dumps polluting our world’s oceans. It was the first to be discovered and is the biggest. It’s located in the middle of the Pacific Ocean between the U.S. states of Hawaii and California, about 1,000 kilometers off the coast of Hawaii. The size of the rubbish heap is difficult to determine. Estimates range from about 15,000 square kilometers (equivalent to the surface area of Antarctica or 8.1% of the Pacific Ocean) to 700,000 square kilometers (almost the surface area of Chile). Let me explain a little more about this sad and unusual phenomenon. The island of rubbish is not a solid island as such, nor a floating sheet of trash. Rather, it’s a soup of plastic particles floating in a gyre. Ocean currents collect thousands of tons of floating garbage and round them up in a giant vortex. The slowly rotating mass prevents the rubbish from dispersing. This soup has everything: abandoned fishing nets, plastic bottles, caps, toothbrushes, shoes and much more. But more than anything, the vortex consists of small particles of plastic created when the waves and sun break down larger pieces. This gigantic mass remains below the surface of the water in a column estimated to extend 30 meters deep. Paradoxically, despite its huge size, the rubbish dump is not easy to visualize as a whole and has not been captured in satellite images because of its location under the water. Worse, it is located in international waters, so no nation is responsible for the waste. After concerned scientists and environmentalists, the only people left to help clean up the mess are passengers on special cruise ships who visit the vortex to help remove some of the rubbish. In all, it’s a gigantic mess going unnoticed, growing slowly but surely in a no man’s land devoid of a god or the rule of law. A chance discovery In 1988, experts from the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration predicted the existence of the garbage patch in the North Pacific Ocean by analyzing local marine currents. But it wasn’t until a decade later when oceanographer Charles Moore officially discovered the trash heap, which was dubbed the "Eastern Garbage Patch." In July 1997, Captain Moore was sailing through the North Pacific Gyre when he came across miles and miles of synthetic pieces of debris, and an immense mass of floating garbage. It took the American one week to cross the accumulation of waste. In 1994, Moore established the foundation Algalita Marine Research to focus on the protection and regeneration of kelp forests and wetlands along the coast of California. But after his floating garbage island discovery, Moore dramatically changed the course of his foundation and dedicated it to raising awareness and promoting education about the garbage patch. (See Moore’s TED talk). Expeditions to the forgotten island Since its discovery, there have been various scientific expeditions to the Great Pacific Garbage Patch and other floating garbage islands like it. Unfortunately, these trips have not managed to generate a significant amount of public awareness or impact outside environmental circles. Nobody seems to be willing to take responsibility or action. The most recent expedition in May was organized by the Society of French Explorers (in French) on a schooner called L’Elan, assisted by Captain Moore on board. The results of the mission have not yet been published. Hopefully now with the ability of social networks to disseminate information widely, the issue will generate more interest and make people aware of the huge amount of plastic we consume. What can we do? As mentioned above, the garbage island mainly consists of billions of plastic pieces too small to be seen. This makes it difficult for the debris to be removed from the ocean. You would have to put a very fine net across the surface of the water, which would disturb the ecosystem and essential marine fauna such as plankton, a key food source for ocean animals. What is more, accessing the polluted area would require a considerable amount of resources including manpower and expensive materials to undertake the difficult work out in the open seas. The task becomes even more unlikely where you consider that the garbage island is located in international waters where no country is sovereign (the tragedy of the commons). For now and until we come up with new technology that lets us travel back in time to prevent this disaster, the best and most sensible thing to do is to stop producing so much garbage, and especially to limit our consumption of disposable plastic. It is also important to help raise awareness of the problem so more people understand the effects of their consumerism, change their lifestyles and educate future generations who will be looking after the planet. The island of trash consists of materials that at one time helped revolutionize the world. Today we are surrounded by plastic: we eat and drink from it. We use it every day. It is present in nearly all of our activities. Plastic is almost a miracle product. Cheap, effective and virtually indestructible, it doesn’t break. It just disintegrates into smaller parts. The considerable durability of plastic means that almost all the plastic molecules ever created still remain somewhere on the planet. Now at least we have a better idea on where they end up: on rubbish island.
Read more
Peru and its socio-environmental conflicts
By María José Veramendi Villa, legal advisor, AIDA, @MaJoVeramendi “In Peru, the general state of social conflict is strongly influenced by the dynamics of economic growth that the country has experienced in recent years; but this growth has not necessarily brought measures that generate a perception of social welfare or political representation for certain sectors of society. ” (Ombudsman’s report No. 156: Violence in social conflict, March 2012) Peru is rich in minerals and other natural resources. Evidence of this is that as of June 2012, 20.3% of the national territory was licensed for mining activities, according to a report by the Cooperación NGO based on data from the government’s Geological Mining and Metallurgical Institute (INGEMMET). In June 2013, the Ombudsman of Peru released its Monthly Report on Social Conflict No. 112 (in Spanish). The report lists 223 registered social conflicts: 170 of which are active (76.2%) and 53 latent (23.8%). While there was a decline in the number of conflicts from the previous month, the most significant and prevalent type of conflict was socio-environmental, of which there were 145 cases in June. Of those cases, 105 were in mining, 18 in hydrocarbons, eight in energy activities and four in forestry projects. The Ombudsman’s office defines social conflict as “a complex process in which different sectors of society, the state and the private sector have conflicting objectives, interests, values or necessities, and that these contractions can lead to violence.” Causes In the 2007 report Socio-environmental Conflicts from Extractive Activities in Peru (in Spanish), the Ombudsman´s office identified at least five causes of these conflicts: People’s justified fear that extractive activities like mining can potentially cause contamination; Communities feel vulnerable living in areas where these activities are being developed; People lack trust in the government’s ability to prevent the contamination and degradation of the environment where they live; Concerns that weak regulations and controls on extractive activities can cause contamination resulting in collateral damages to third parties, imposing higher costs on activities like agriculture, whose existence and development can be jeopardized by the decline in quality or quantity of available water; and The negative impacts of extractive activities. These causes are as pertinent today as they were in 2007. But the Peruvian authorities still appear to ignore the situation, and, in response, the justified fear of the population and the mistrust in the state worsen. A recent example: The implementation of prior consultation Convention No. 169 (in Spanish) of the International Labour Organization (ILO) came into force in Peru on February 2, 1995. Since then the country has been obligated to comply with its provisions, which enforce, among others, the right of indigenous and tribal peoples to be consulted onissues that affect them. The convention also states that these people, in a prior, free and informed manner, can participate in the processes to develop and formulate policies that affect them. According to the jurisprudence of the Peruvian Constitutional Court, the convention has constitutional status. Despite this, its implementation was non-existent to the point of being a systematically denied right in the country until August 23, 2011. That’s when the Peruvian Congress approved legislation on the right to prior consultation for indigenous and tribal peoples. The law was promulgated and published on the September 6, 2011, and it has been in effect since December of that year. The Rules of Procedure to apply the Law were issued on April 3, 2012 and put into force a day later. But these legal instruments, which could be seen as an act of good faith to implement norms that already exist in our legal system, have been heavily criticized for technical failures and for reducing the standards of protection achieved by indigenous people through their many years of struggle. These protections were cemented in the ILO Convention No. 169 of 1989, the United Nations Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples (2007) and in the jurisprudence of the international bodies set up to protect human rights, especially the Inter-American Court of Human Rights I want to highlight two facts on these shortcomings: First, the Rules of Procedure of the Consultation Law only applies to acts conducted after its approval. This means that during the 16 years between the approval of Convention No. 169 and the Consultation Law and its Rules of Procedure, the former was merely a decorative instrument. The second little-known fact is that the Judgment 00025-2009-PI/TC (in Spanish) of the Constitutional Court states specifically: “The enforceability of the right to consultation is linked to the implementation of the ILO Convention 169 in our legal system." Government officials (in Spanish) have signaled that the Law of Prior Consultation is not binding. Even the Peruvian president said the law “should be viewed as an instrument allowing investment, and to not to be seen as an obstacle.” We remember that in the case of The Kichwa Peoples of Sarayaku Vs. Ecuador, the Inter-American Court of Human Rights ruled that proper consultation is a general principle of international law. It’s time to be alert. The proper implementation of the right to consultation and prior, free and informed consent is the key to developing effective protection of indigenous rights. In a country where socio-environmental conflict is the norm – along with the causes mentioned above, it is essential to build trust and confidence among the population and give assurances that their rights will be safeguarded. If these points are not put into action, it would be no surprise to see a surge of conflicts in future.
Read more
Organizations call for probe into the murder of Jairo Mora in Costa Rica (Spanish only)
In a letter to Costa Rican General Attorney Jorge Chavarría and René Castro, the minister of environment and energy, local and international organizations expressed deep concern for the murder of Jairo Mora, a young defender of the leatherback sea turtles. He was murdered on May 30, 2013 in Moín Beach, Limón province. The groups said the severity of the crime warrants an immediate and effective investigation to prevent impunity and the repetition of such acts. The following are essential: A serious, impartial, immediate and effective investigation must be carried out to put on trial and punish the individuals responsible for Jairo Mora's murder. Measures must be taken so that the authorities responsible for controlling and monitoring the environment can effectively guarantee the rights of environmentalists, offering adequate support including through patrols to protect natural resources and by earmarking sufficient resources for these purposes. The state must publicly recognize the importance of the work of environmentalists as defenders of human rights, and it must take the necessary measures to stop the violence against them by taking an active position of respect and protection of their rights. In the last paragraph of the letter, the organizations write that “impunity in cases of serious aggression against advocates for defending the environment and natural resources is not only a violation of human rights but also presents a serious threat against environmental sustainability. Therefore, it is necessary for Costa Rica, as a nation committed to defending the environment, to take effective action to prevent such crimes like Jairo Mora's murder don’t go unpunished and don’t happen again.”
Read more