
Project
Liliana Ávila /AIDAMayan women’s struggle before the Inter-American Development Bank in Guatemala
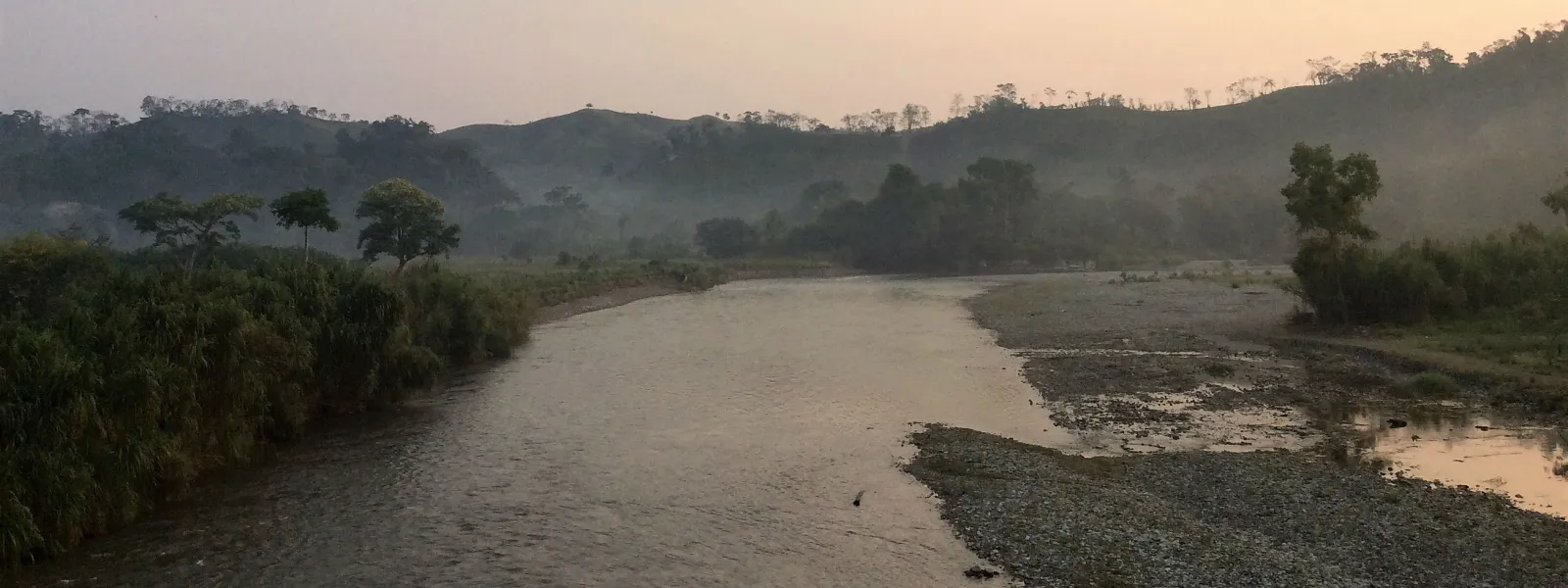
Mayan communities succeeded in getting the IDB Invest to develop a responsible exit plan after withdrawing its financing for two hydroelectric projects that negatively impacted ecosystems and the livelihoods of indigenous peoples, especially women, in the micro-region of Yichk'isis (Ixquisis).
In the struggle to defend their water, territory and way of life, indigenous Mayan communities in the Yichk'isis (Ixquisis) micro-region of northern Guatemala convinced the Inter-American Development Bank Group to withdraw its financing of two hydroelectric dams whose implementation violated their rights. The decision was also significant in that the IDB, for the first time, designed a responsible exit plan.
That historic advance was the result of the complaint that the communities filed in August 2018—with the support of AIDA, the Plurinational Ancestral Government of the Akateko, Chuj, and Q'anjob'al Native Nations, and the International Platform against Impunity. The complaint was filed with the Independent Consultation and Investigation Mechanism (MICI), the IDB Group's accountability office.
In resolving the case in September 2021, the MICI concluded that IDB Invest failed to comply with its own operational policies and safeguards, in the framework of the financing granted to the company Energía y Renovación S.A. for the implementation of the San Mateo and San Andrés hydroelectric projects.
Learn more about this achievement
In the mountains of Northwestern Guatemala, near the border with Mexico, the land is rich and fertile. Several important rivers and many other water sources feed the soil.
The residents of these mountains, many indigenous women of Mayan descent, have long depended on the waters to nourish them, to provide them with fish, as well as for agriculture, sanitation, and cooking.
But the construction of the San Mateo and San Andres dams has caused water scarcity and the contamination of rivers and other natural resources long cherished by the communities.
The near lack of water has also drastically reduced harvests, lessening the income gained from selling corn, wheat, beans, coffee, sugar cane and other products in the market. As a result, the conditions of poverty in the area have deepened.
And the risk situation is profound, particularly for women, who have played a very important role in the defense of water and territory threatened by hydroelectric projects, and are therefore victims of intimidation and stigmatization.
As guardians of their land and water, they have come to its defense and they’ll continue to prevent environmental deterioration from further harming their families.
Read our fact sheet on the case

Related projects

Applauding the exclusion of Eletrobras from Norwegian oil fund
The Council on Ethics, which governs the world's largest sovereign wealth fund, recommended the exclusion due to the participation of the Brazilian state-owned company in the Belo Monte hydroelectric project, which is associated with serious human rights violations against indigenous peoples. On May 13, the Norwegian oil fund, considered the world's largest sovereign wealth fund, excluded twelve companies from its investment portfolio for ethical reasons, including Brazil's Eletrobras for its participation in the Belo Monte hydroelectric project. The fund is managed by the public bank Norges Bank Investment Management, which follows the recommendations made each year by the Ethics Council to ensure that investments meet certain criteria. The Council noted that the Belo Monte project, run by the Norte Energia consortium - of which Eletrobras is a part - caused "greater pressure on indigenous lands, the disintegration of the social structures of indigenous peoples and the deterioration of their ways of life" with the forced displacement of some 20,000 people. AIDA - as part of a joint civil society effort - informed the Council of the situation of the indigenous and riverine populations affected by the project, its social and environmental impacts, the operational situation of the dam, and the current status of national and international legal actions brought against the project. We believe the Council's decision should be applauded because it discourages the continuation of unsustainable and ill-named development projects that threaten the survival of indigenous and traditional peoples, as is the case with Belo Monte. It is essential that banks, international financial institutions and monetary funds take into account the likely impacts of the projects they finance. Supporting socially and environmentally sustainable projects instead of initiatives that prioritize economic benefit over the protection of human rights and the environment demonstrates responsible and ethical investment. PRESS CONTACT Victor Quintanilla, [email protected], +5215570522107
Read more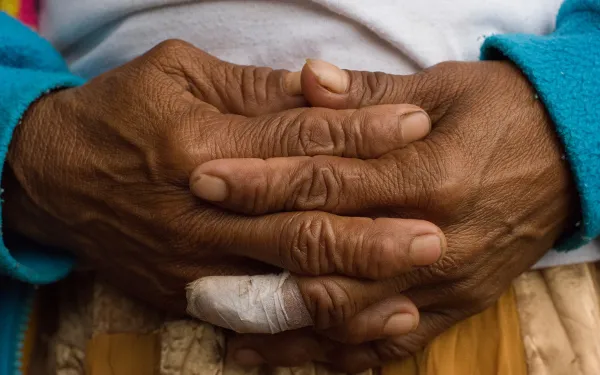
Inter-American Court upholds indigenous rights in Argentina
In Argentina’s Rivadavia department, along the border of Bolivia and Paraguay, the lands have been inhabited by indigenous people for at least 60 years. Communities there subsist primarily from hunting, gathering, and fishing. Many of these ancestral peoples have been battling for governmental recognition of their land rights since 1984, when the country’s transition from dictatorship to democracy began. This lack of recognition has had profound impacts on the lives of indigenous inhabitants, affected by changes in their land and its use. As Creole families settled in the area, they brought their own customs and economic activities, such as animal grazing and illegal logging. Barbed wire fence was erected without consulting indigenous populations, and an international bridge was built that crosses into their land. These developments have changed how the indigenous people eat and disrupted their access to water, threatening their very cultural identity. With no protection from the Argentine government, in 1998 a coalition of indigenous groups took their struggle before the Inter-American Commission on Human Rights. Grouped in the Lhaka Honhat (Nuestra Tierra) Association—made up of Wichí (Mataco), Iyjwaja (Chorote), Komlek (Toba), Niwackle (Chulupí) and Tapy'y (Tapiete) indigenous peoples—, they were represented by the Centre for Legal and Social Studies. In 2012, the Commission issued its Merits Report, establishing the violation of indigenous communities' rights and recommending that the State adopt reparation measures. When Argentina failed to comply with the provision, the case was referred to the Inter-American Court of Human Rights. On April 2, 2020, the Court’s decision declared Argentina responsible for the violation of the indigenous peoples’ rights to community property, cultural identity, a healthy environment, and adequate food and water. The ruling marks an important milestone in the struggle for indigenous rights. It is the first time that the Court, in a contentious case, has analyzed these rights autonomously on the basis of Article 26 of the American Convention, and ordered specific measures for their restitution, including actions for access to food and water, the recovery of forest resources, and the recovery of indigenous culture. Actions for Reparation Among other implications, the Court's decision could lead to solutions to the health issues afflicting the indigenous communities of Lhaka Honhat. The violation of their rights to food and water has caused deaths from malnutrition and dehydration. The Court demanded that the State present a study within six months that identifies critical situations of lack of access to drinking water and food, formulates a plan of action to address them, and begins its implementation. It also ordered the creation and implementation of a community development fund within a period of no more than four years. As for the territory, the State shall, within a maximum period of six years: Delineate, demarcate, and grant a single collective title without subdivisions or fragmentations for the indigenous communities. Transfer the Creole population out of the indigenous territory through specific mechanisms that promote, above all, voluntary transfer. Remove barbed wire fences and livestock belonging to Creole settlers from indigenous lands. Refrain from carrying out acts, works or undertakings in indigenous territory. Additionally, the Court requested the adoption of legislative and/or other measures to provide legal certainty to the right to indigenous community property in Argentina. Supporting the Indigenous Struggle In March 2019, AIDA helped author and amicus brief in support of the climate of the indigenous communities of the Lhaka Honhat Association. We did so alongside our allies on the litigation group of the International Network for Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (ESCR-Net), including Amnesty International, the Asociación Civil por Igualdad y Justicia, the Colombian Commission of Jurists, Dejusticia, FIAN International, International Women's Rights Action Watch - Asia Pacific, and the Minority Rights Group International. Our arguments highlighted the importance of recognizing economic, social, cultural, and environmental rights as real enforceable rights—similar to others such as the right to life or personal integrity—due to their independent and indivisible nature. In this sense, AIDA recalled the important advance that the Court promoted with Advisory Opinion 023, which recognizes the right to a healthy environment as fundamental to human life. Our brief called on the government to respect the rights of indigenous peoples—as outlined in Article 26 of the American Convention on Human Rights—to a healthy environment, food and water, and cultural identity. The Court's decision establishes an important regional precedent for the protection of the environment in the Americas. It contributes to the consolidation of standards to protect the land of indigenous communities, as well as their rights to a healthy environment, water and culture.
Read more
Inter-American Court upholds indigenous rights in Argentina
In Argentina’s Rivadavia department, along the border of Bolivia and Paraguay, the lands have been inhabited by indigenous people for at least 60 years. Communities there subsist primarily from hunting, gathering, and fishing. Many of these ancestral peoples have been battling for governmental recognition of their land rights since 1984, when the country’s transition from dictatorship to democracy began. This lack of recognition has had profound impacts on the lives of indigenous inhabitants, affected by changes in their land and its use. As Creole families settled in the area, they brought their own customs and economic activities, such as animal grazing and illegal logging. Barbed wire fence was erected without consulting indigenous populations, and an international bridge was built that crosses into their land. These developments have changed how the indigenous people eat and disrupted their access to water, threatening their very cultural identity. With no protection from the Argentine government, in 1998 a coalition of indigenous groups took their struggle before the Inter-American Commission on Human Rights. Grouped in the Lhaka Honhat (Nuestra Tierra) Association—made up of Wichí (Mataco), Iyjwaja (Chorote), Komlek (Toba), Niwackle (Chulupí) and Tapy'y (Tapiete) indigenous peoples—, they were represented by the Centre for Legal and Social Studies. In 2012, the Commission issued its Merits Report, establishing the violation of indigenous communities' rights and recommending that the State adopt reparation measures. When Argentina failed to comply with the provision, the case was referred to the Inter-American Court of Human Rights. On April 2, 2020, the Court’s decision declared Argentina responsible for the violation of the indigenous peoples’ rights to community property, cultural identity, a healthy environment, and adequate food and water. The ruling marks an important milestone in the struggle for indigenous rights. It is the first time that the Court, in a contentious case, has analyzed these rights autonomously on the basis of Article 26 of the American Convention, and ordered specific measures for their restitution, including actions for access to food and water, the recovery of forest resources, and the recovery of indigenous culture. Actions for Reparation Among other implications, the Court's decision could lead to solutions to the health issues afflicting the indigenous communities of Lhaka Honhat. The violation of their rights to food and water has caused deaths from malnutrition and dehydration. The Court demanded that the State present a study within six months that identifies critical situations of lack of access to drinking water and food, formulates a plan of action to address them, and begins its implementation. It also ordered the creation and implementation of a community development fund within a period of no more than four years. As for the territory, the State shall, within a maximum period of six years: Delineate, demarcate, and grant a single collective title without subdivisions or fragmentations for the indigenous communities. Transfer the Creole population out of the indigenous territory through specific mechanisms that promote, above all, voluntary transfer. Remove barbed wire fences and livestock belonging to Creole settlers from indigenous lands. Refrain from carrying out acts, works or undertakings in indigenous territory. Additionally, the Court requested the adoption of legislative and/or other measures to provide legal certainty to the right to indigenous community property in Argentina. Supporting the Indigenous Struggle In March 2019, AIDA helped author and amicus brief in support of the climate of the indigenous communities of the Lhaka Honhat Association. We did so alongside our allies on the litigation group of the International Network for Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (ESCR-Net), including Amnesty International, the Asociación Civil por Igualdad y Justicia, the Colombian Commission of Jurists, Dejusticia, FIAN International, International Women's Rights Action Watch - Asia Pacific, and the Minority Rights Group International. Our arguments highlighted the importance of recognizing economic, social, cultural, and environmental rights as real enforceable rights—similar to others such as the right to life or personal integrity—due to their independent and indivisible nature. In this sense, AIDA recalled the important advance that the Court promoted with Advisory Opinion 023, which recognizes the right to a healthy environment as fundamental to human life. Our brief called on the government to respect the rights of indigenous peoples—as outlined in Article 26 of the American Convention on Human Rights—to a healthy environment, food and water, and cultural identity. The Court's decision establishes an important regional precedent for the protection of the environment in the Americas. It contributes to the consolidation of standards to protect the land of indigenous communities, as well as their rights to a healthy environment, water and culture.
Read more